A heat wave that left greater than 100 million people sweating within the eastern United States in June 2024 hit so fast and was so intense that forecasters Drought warning given. Can follow in wide parts of the world.
Prolonged high temperatures can quickly dry out soils, triggering rapid droughts that may affect agriculture, water resources and energy supplies. Many areas developed rapidly under the June heat dome. Exceptionally dry conditions.
NOAA Climate Prediction Center
The human impact of the warmth wave has also been large-scale. In Ohio and Pennsylvania, Emergency room visits For heat-related illnesses. Several Massachusetts School closed without air conditioning For the security of kids and teachers. In New York and New Jersey, The electric wires got burnt in the heat.shutting down trains out and in of New York City and leaving passengers stranded.
We read Weather patterns Heat included. The June 2024 heat wave was unusually early and long-lasting as compared. General pattern For the northeastern United States
It was attributable to a big high-pressure system called a heat dome that prolonged greater than 10 miles into the atmosphere from the bottom. A heat dome is each a cause and an effect of maximum heat. In very large and powerful heat domes, equivalent to the Northeast event – which has reached more into the atmosphere than any previous event in June – higher temperatures usually tend to affect more people.
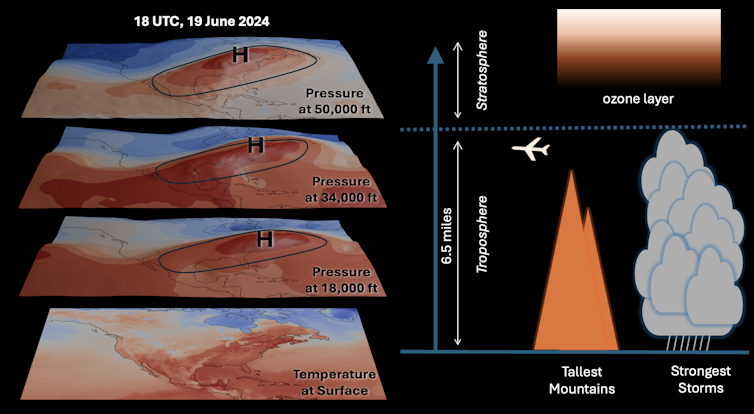
Matthew Barlow, University of Massachusetts Lowell
It was also a part of a worldwide outbreak of early-season heatwaves that threatened lives in lots of countries world wide.
Heat is becoming a worldwide problem.
In 2024, record heat has affected many countries in America, Europe and Asia. Weeks of persistent heat in Mexico and Central America, with temperatures reaching 125 degrees Fahrenheit (51.8 Celsius), combined with prolonged drought Severe water shortages and dozens of deaths.
The intense heat in Saudi Arabia became a tragedy. More than a thousand people on Hajja Muslim pilgrim in Mecca, collapsed and died. The temperature reached 125 F (51.8 C). On June 17 on the Grand Mosque in Mecca.
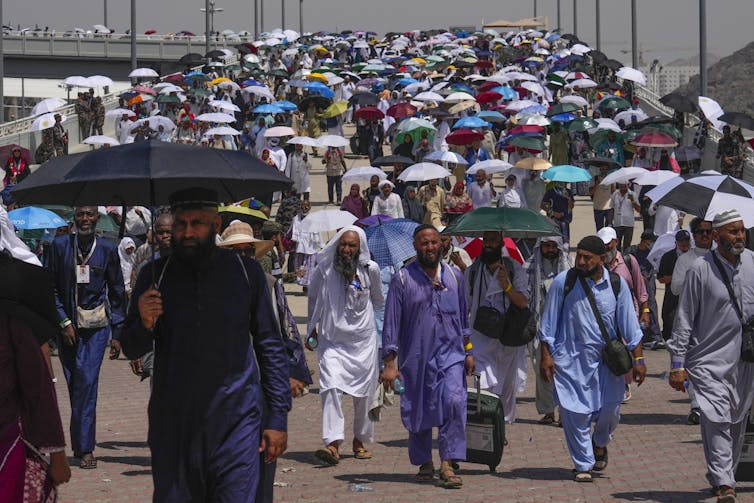

AP Photo/Rafiq Maqbool
In Greece, where temperatures exceeded 100 F (38 C) for several consecutive days in June, a minimum of Many tourists Died or feared dead after climbing in dangerous heat and humidity.
India also experienced temperatures around 120 F (49 C) for days in April and May affecting thousands and thousands of individuals, lots of whom were without air-con.
Climate Related: This shouldn’t be common.
Although heat waves are a natural a part of the climate, the intensity and extent of warmth waves thus far this yr shouldn’t be “just summer.”
A scientific review of the US heat wave concluded that the warmth was intense and long-lasting. Two to four times more likely Today wouldn’t exist without it as a result of human-caused climate change. This result’s consistent with that. Rapid growth The variety of heat waves within the United States over the past several a long time and their occurrence outside the summer peak.
These record heat waves are occurring in a climate that’s 2.2 F (1.2 C) warmer globally than it was before the Industrial Revolution, when humans began emitting large amounts of greenhouse gases which have warmed the climate. Heats the air.
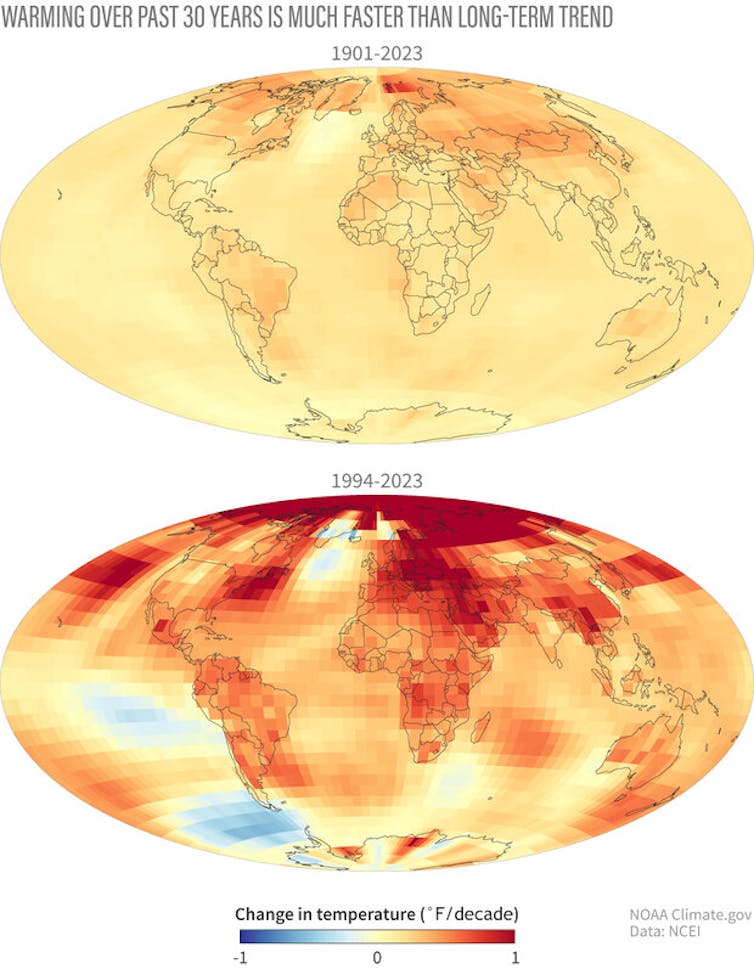
NOAA NCEI
A temperature difference of 1 or two degrees will not be noticeable whenever you move into one other room, but even fractions of a level make an enormous difference in global climate.
At the peak of the last ice age, about 20,000 years ago, when the northeastern United States was under hundreds of feet of snow, the common global temperature was only 10.8 F (6 C) cooler than it’s now. So, it's not surprising that 2.2 F (1.2 C) of warming thus far is already rapidly changing the climate.
Countries promised in 2015. As a part of the Paris Agreement to maintain warming below 2C, but current government policies world wide will not meet these objectives.. Temperatures proceed to rise, with this increase prone to double again by the top of the century.
If you’re thinking that it's hot.
While this summer is probably going certainly one of the most well liked on record, it's necessary to understand that it may be certainly one of the coldest summers in the long run.
For populations which can be particularly vulnerable to heat, including young children, older adults and outdoor employees, the risks are even greater. i people Low-income neighborhoods Where air-con will be unaffordable and tenacious. which often do not have the same considerations for cooling as heating You can have to face dangerous situations.
Extreme heat also can affect economies. It can bind rail tracks and cause wires to bend, This causes transit delays and disruptions.. It can try this too. Overload electric system with high demand And cause blackouts when people need cooling essentially the most.
The excellent news: There are solutions.
Yes, the long run is bleak in a warming world. However, countries have made significant progress. In the US, the 2022 De-Inflation Act has this potential. Cut U.S. greenhouse gas emissions by nearly half by 2035.
Converting air conditioners to heat pumps and Network geothermal system It cannot only reduce fossil fuel emissions but additionally provide cooling at a lower cost. gave The cost of renewable energy The fall continues, and plenty of countries have Increased policy support and incentives.
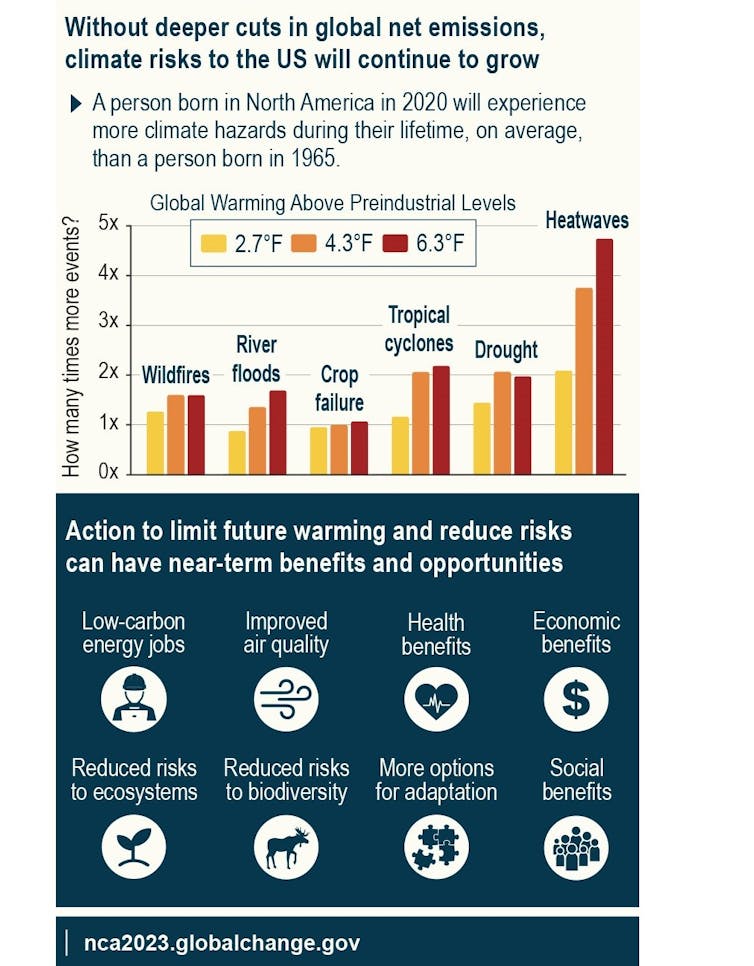
National Climate Assessment 2023
Humanity can do loads to limit future warming if countries, corporations and individuals are in all places. Act immediately. Rapidly reducing fossil fuel emissions may help avoid a hotter future with worst heat waves and droughts, while improving public health, creating jobs and reducing threats to ecosystems, amongst other things. Benefits might also be provided.














Leave a Reply