For a long time, military doctors faced a very important challenge: What is the perfect method to safely and effectively deliver oxygen to patients in distant war areas, rural hospitals or destruction?
Oxygen tanks are heavy, expensive and dangerous in combat areas. Directly hitting missiles or tablets can turn life -saving resources right into a deadly risk.
Naval General Ernest Tok Cook once said“Logistics is a difficult part of fighting war.” It is ahead of oxygen. In order to deploy US troops, available throughout the fighting for the treatment of wounded soldiers can mean the difference between life and death.
The Defense Department turned to military physicians and academic researchers in military medicine University of Colorado Center for War ResearchTo study whether the military must bring oxygen to the battlefield for soldiers – and, if, how much.
This approach to research is often known as the military-sail contribution. The purpose of those partnerships is to avoid wasting lives on the battlefield. But they save lives throughout the United States by changing military medical advantages for higher health care.
Innovations and curse
In the civilian world, it takes Average 17 years Investigative discovery to alter medical practice. One of probably the most famous examples is using tranexamic acid for traumatic patients. Transamic acid is Injected to prevent bleeding During surgery or after trauma. It was discovered in 1962 but was not approved by the FDA until 1986. These Was not used to bleed By 2012.
The changing nature of the war and threats against US forces need military medicine to maneuver forward. War injuries and infection researchers put pressure to search out higher ways to avoid wasting lives, which are sometimes faster than urban health care.
Via partner/anadolu gettyimages
In the middle, scientists work Side with military medical teams Fields of the battlefield, development and test solutions.
Wish they were To address the use of oxygenFor, for, for, for,. Painful brain injuriesBurn treatment or Trauma careThis partnership allows military and civilian researchers to quickly formulate discoveries.
Re -considering oxygen
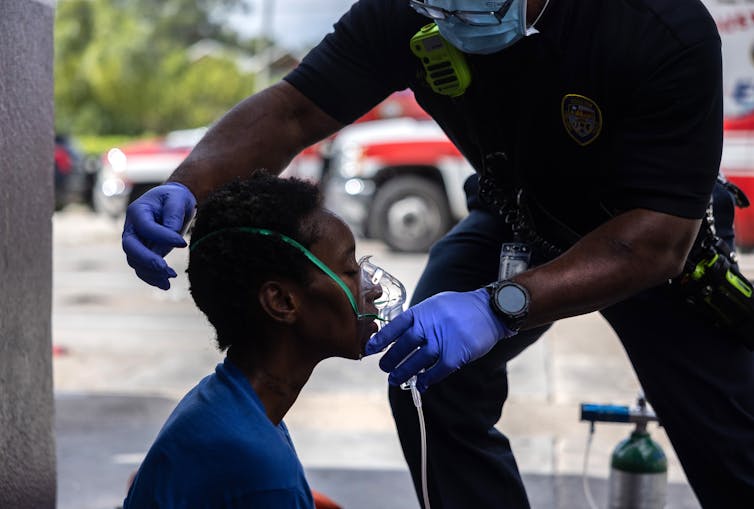
Instant administration of oxygen An injured or sick patient has long been the inspiration stone of trauma and burning. The logic seemed easy: When the patients were in shock or seriously injured, their bodies struggle to get enough oxygen, so doctors provided more money.
Our research, and others, found a variety of Oxygen can actually be harmful. Extra oxygen stimulates oxidate stress – a high burden of unstable molecules called free radicals Can damage healthy cells. It can result in more inflammation, slow healing and even organ failure.
In short, while oxygen is crucial, it isn’t all the time higher.
We launched a series of military-mutual cooperation with a reputation named Strategies to avoid excessive oxygen, or savings O2. We discovered that seriously injured patients Often requires low oxygen More than previously convinced, 95 % of those patients need less or no additional oxygen for protected care.
This search challenges the normal medical wisdom of a long time. This will give a brand new appearance on how medical professionals approach not only military settings, but in addition in civilian hospitals.
Within a 12 months of Military medical leaders present their searches in front ofThis insights exist already Affected changes and update to the patient Decisions related to care leaders, medical training and even the acquisition of medical equipment.
Increasing our results L Wee, we’ve began a trial to be used of use Artificial intelligence to automate oxygen delivery. This military -funded study can take higher care of wounded soldiers and ambulances or injured civilians in distant areas, before they reach major references and trauma centers.
John Moore/Gateati Magizes
In rural or distant areas of the United States, access to additional oxygen may be limited because of supply chain challenges, high costs and shortages. It is Is particularly true in small hospitals And affects the primary respondents after a natural disaster or accident. In the intensive care units of those hospitals, using oxygen can preserve limited oxygen supply for patients who use more effectively.
Long -term John Damage Care: A New Frontier
Investigating oxygen needs within the combat zone, we realized one other pressing problem: long -time crashing challenges. During a dispute, military health workers often must treat seriously injured soldiers for hours or days before evacuating the injured person.
In the longer term dispute with the “nearest toe” like China or Russia, there will not be the power to quickly evacuate wounded soldiers within the United States. Without transporting reliable helicopter or aircraft, many casualties may not reach trauma care Within the “Golden Hours”. This is significant for the primary 60 minutes after severe injury, when rapid treatment is crucial.
The ongoing war in Ukraine has explained that Long -term Loose Damage Care Challenge. In Ukrainian hospitals, doctors are having trouble treating the injuries of urban and military patients for this reason Increased antibiotic resistance.
Military conflicts in the longer term Will present the Indo -Pacific area Similar challenges, including long -term transportation times and long -term care brought on by accident care.
However, this challenge isn’t unique within the battlefield. Civilian crises have long been cared for by the accident. For example, during a natural disaster, emergency respondents should manage patients without immediate access to hospitals.
Once patients are treated in the sector or within the scenario of destruction, suppliers should often maintain care with limited resources. They have to provide priority to the vital interference, minimize using resources and stabilize patients for a high level of take care of patients.
Innovation in health care is promoted to mutual cooperation. Military-Islamic Partnership is a method to advance the medical solution in a faster and more practical way. These innovations save life in fighting, improve care and permit us to use our 98 % of survival rate in war For our traumatic centers, rural hospitals and disaster zones within the United States














Leave a Reply