what’s
is a standard fungal plant pathogen that causes problems for farmers across the United States
It causes a disease in barley and wheat Head blight, or scabies. It may also damage rice and maize ears and stalks. In severe cases, scab can reduce a farm's production by 45%.
Martin Chilors/Michigan State University
Scab has been liable for some great annuals Crop losses In the U.S. in 2024, projections by Extension and Research plant pathologists suggest that scab has reduced the U.S. wheat crop. About 31 million bushels Or about 22%.
When in comparison with other diseases of wheat that damage the top and kernel, scab is by far a very powerful since it occurs over wide areas and affects the crop at advanced stages of development.
Why the priority?
As a plant pathogen, the fungus liable for scab produces a Mycotoxins in grains that may harm humans and livestock. Also, when wheat grain used for seed is infected with the fungus, the seeds are less prone to germinate and produce recent plants in the subsequent growing season.
Mycotoxins are widespread Classified as a vomitoxin. It may induce vomiting if ingested in sufficient concentrations, but prolonged exposure might also cause gastrointestinal damage, Damaged immune system and inflammation of the central nervous system.
In animals, repeated exposure to mycotoxins in food can reduce their growth and weight, and livestock support Create an immune response to toxins that may impair their ability to breed.
The US Food and Drug Administration has Advisory level issuedprimarily limits the quantity of mycotoxins considered a health hazard in cereal products.
Since barley and wheat are essential as food for humans and livestock, so is harvested grain Routinely tested When farmers bring their crops to grain elevators on the market. Entire a great deal of grain could also be rejected in the event that they are found to contain mycotoxin concentrations above FDA limits.
Wheat Can be treated To remove itchy pimples. If the mycotoxin level isn’t too high, it may well even be used for livestock feed. The advisory threshold for mycotoxins is higher for adult cattle and poultry, at 10 parts per million, than for humans, at 1 ppm.
What does the law say about importing and transporting plant pathogens?
These are the risks that the U.S. Department of Agriculture's Animal and Plant Health Inspection Service, or USDA-APA, controls to import and even transport plant pathogens throughout the United States. Plant Protection Act 2000.
Federal law prohibits the movement of plant pathogens, including bacteria, fungi and viruses, even for research purposes, in addition to their release into the environment. A scientist who desires to transfer a plant pathogen, either throughout the United States or from outside the United States, must undergo a permit process. USDA-APHIS It may take six months to finish.

Jeffrey Greenberg/Universal Images Group via Getty Images
The goal of those rules is to cut back the chance of introducing a brand new species that might be much more destructive to crops.
Even this, which has appeared on every continent but Antarctica, has the potential to introduce recent genetic material into the environment which may be present in other countries but not within the United States and will have harmful consequences for crops.
How do you manage the infection?
Infections normally occur during flowering, rain and periods of plants High humidity During the early stages of grain production.
Wheat in South America is prone to infection throughout the spring. As the season progresses, The threat from scabies progresses north In the U.S. and Canada as grain crops mature across the region, with consistent periods of favorable weather throughout the summer.
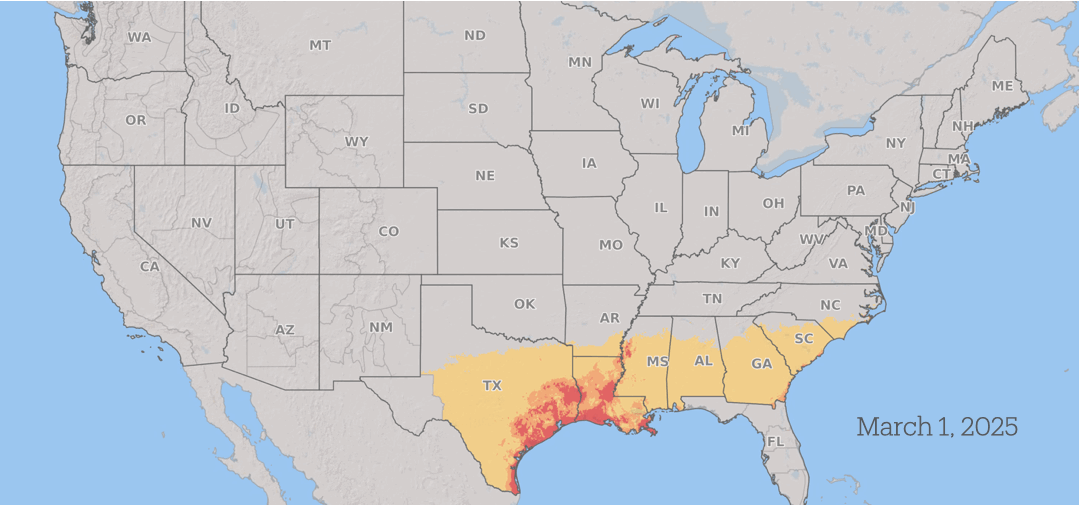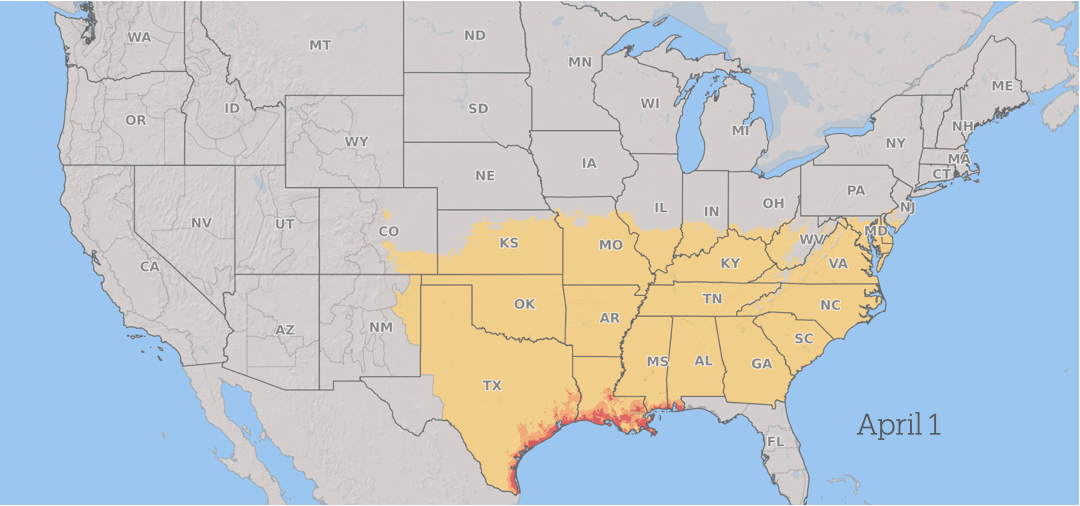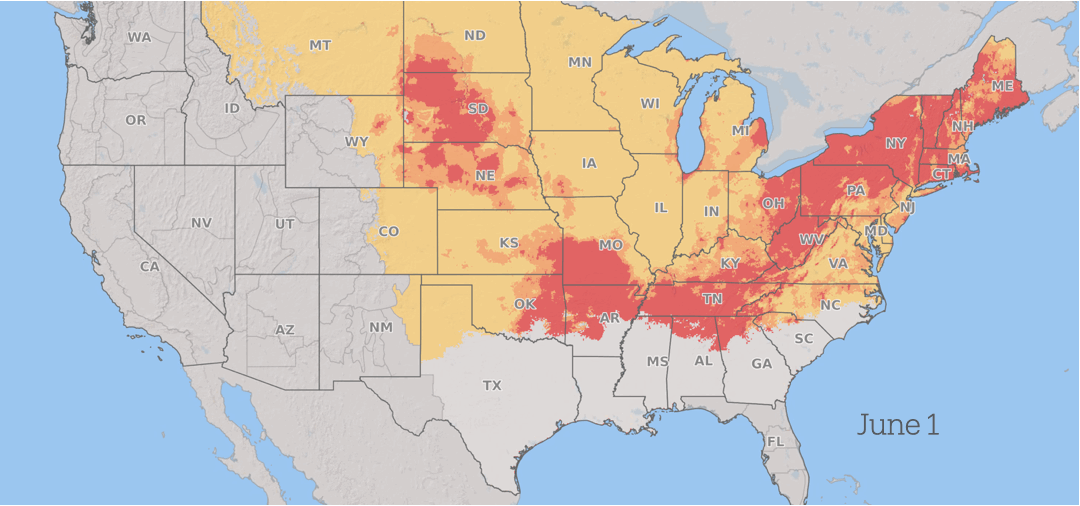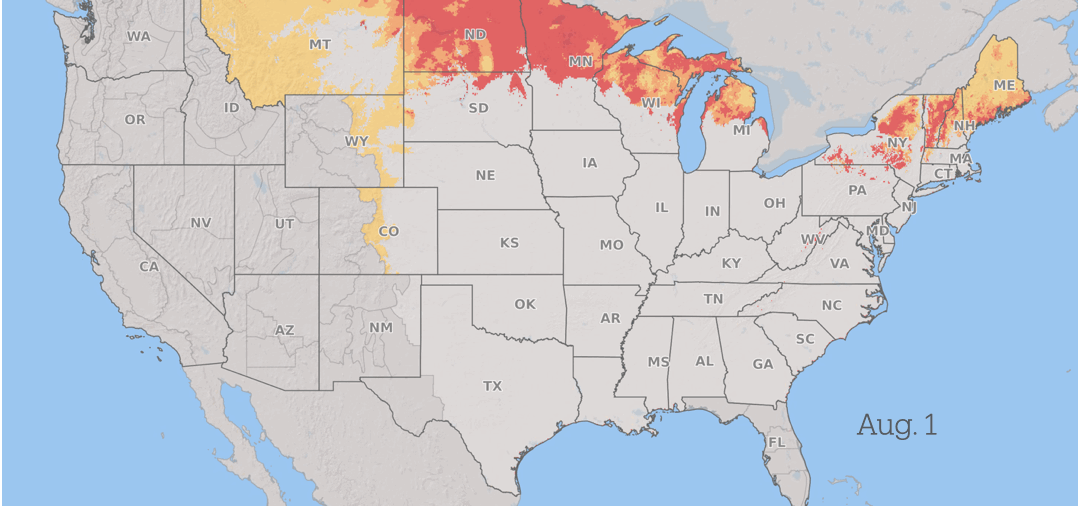
Between seasons, barley, wheat, and corn survive on plant residues that remain in the sphere after harvest. It reproduces by producing microscopic spores After that, you can travel long distances On wind currents, spreading the fungus over large geographic areas each season.
In wheat and barley, growers spray fungicides on developing wheat heads to suppress damage. When they’re most prone to infection. Fungicide application May reduce itching and its severityimprove grain weight and reduce mycotoxin contamination.
However, integrated approaches to managing plant diseases are often ideal, including planting barley or wheat varieties which can be proof against scab and using rigorously timed fungicide applications, rotating crops, and post-harvest soil to cut back residues where they will survive the winter.
Although fungicide applications will be helpful, fungicides offer just some protection and can’t cure scab. If environmental conditions are extremely favorable for scab, with sufficient moisture and humidity during flowering, the disease will still occur at a low level.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ofhtnjqikeo
Plant pathologists are developing an early warning system for farmers. A team from Kansas State University, Ohio State University and Pennsylvania State University is developing a pc model to predict the chance of scabies. Their wheat disease Predictive model Uses current conditions in addition to historical and current atmospheric data from weather stations across the United States to supply a forecast.
In areas most in danger, plant pathologists and commodity experts encourage wheat growers to use fungicides in periods when the fungus is more than likely to grow to cut back crop damage and mycotoxin spread.














Leave a Reply